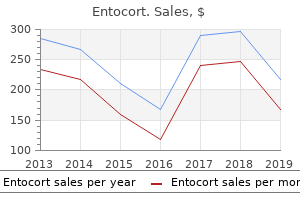
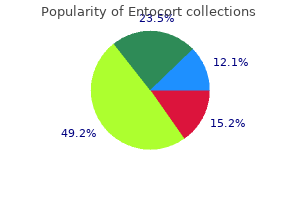
"Buy entocort, allergy shots water retention".
By: D. Roland, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Professor, Tulane University School of Medicine
It is important that physicians caring for elderly patients in nursing homes allergy shots versus medication generic entocort 200 mcg mastercard, treating disabled patients in whom a pelvic examination may be difficult allergy treatment for 6 month old order entocort in united states online, and acting as the primary care physician for women not seeing a gynecologist perform Pap smears on a regular basis or ensure that another physician has done so allergy map buy cheap entocort 200 mcg on line. Simple attention to this mandate could substantially reduce the already low incidence of invasive cancer in U allergy forecast jerusalem israel discount 100 mcg entocort free shipping. Screening for endometrial cancer precursors has been attempted via a cytologic approach, but endometrial cancer precursors lack the easy-to-identify cytologic alterations that permit cervical cancer screening to be carried out with relative ease. Most attempts at screening (which, by definition, is carried out in an asymptomatic population), either by cytology or by endometrial biopsy, have foundered because of the low detection rate in asymptomatic women and because of the high false-positive rate when endometrial cytology is used as a screening technique. For these reasons, organized programs for endometrial cancer screening have not been promulgated on a population-wide basis. Even in high-risk groups such as obese, hypertensive, or estrogen-treated patients, endometrial cancer screening is not generally recommended. Detection of endometrial cancers and their precursors has instead concentrated on educating physicians and patients about the need for biopsy in any patient who has signs and symptoms that may point to an abnormality in the endometrial cavity. Because endometrial hyperplasia and cancer are commonly associated with abnormal patterns of uterine bleeding, it is universally recommended that any patient with menorrhagia, metrorrhagia, or postmenopausal or other unexplained vaginal bleeding be evaluated and that the evaluation include at least an endometrial biopsy. Ultrasonography, with its ability to identify the thickness of the endometrium, has also been used to examine patients with abnormal uterine bleeding and, in some instances, has been suggested as a potential screening procedure for endometrial cancer and its precursors. A diagnosis of endometrial cancer or its precursors is most commonly established after patient self-referral for postmenopausal, intermenstrual, or excessive uterine bleeding. Despite the fact that bleeding is a non-specific symptom of endometrial pathology, about 10% of postmenopausal women who bleed have endometrial cancer. To detect as many cancers and their precursors as possible, even a transient episode of vaginal bleeding or spotting in postmenopausal women or any abnormal vaginal bleeding pattern in perimenopausal women must be evaluated in timely fashion. In such patients, endometrial biopsy is usually used as the initial diagnostic procedure, and the patient is generally only monitored if it is negative. If the patient continues to be symptomatic, however, hysteroscopy and endometrial curettage are advocated as the next 1381 diagnostic procedure, and other causes of bleeding should be evaluated. Kurman R, Soloman D: the Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical/Vaginal Cytologic Diagnoses. Definitions, Criteria, and Explanatory Notes for Terminology and Specimen Adequacy. The age-specific incidence gradually rises and reaches a peak at about age 70, at which time the incidence is 55 per 100,000 among white women. The cause of ovarian cancer is unknown; except for some relatively rare familial groups, it has not been possible to identify any clinically useful high-risk groups for increased surveillance. Rare familial groups with a high incidence of ovarian, breast, and colon cancer have been described. Multiple pregnancies and the use of oral contraceptives may be protective because of decreased ovulation and hormonal influences. These tumors account for almost 90% of ovarian cancers and are most commonly found in postmenopausal women. These tumors are usually unilateral and may occur in any age group, but most typically in the 4th and 5th decades. Surgical excision alone may be all the therapy required, but combination chemotherapy is effective for metastatic or recurrent disease. In some cases, a pelvic mass is the 1st indication of a primary gastrointestinal or endometrial carcinoma. Occasionally, ovarian enlargement is found on routine examination, and cancer may be discovered incidentally at the time of abdominal or pelvic surgery for other indications. In two thirds of patients, however, widespread intra-abdominal metastases are present by the time the diagnosis is made. Symptoms of abdominal swelling, bloating, and pelvic fullness or pressure are common. It is not unusual for the patient to have had vague abdominal complaints or non-specific gastrointestinal symptoms. The presence of an irregular mass in the pelvis or cul-de-sac nodularity accompanied by ascites is often diagnostic. Malignant pleural effusions develop in some patients, and they initially seek medical attention for shortness of breath. Transvaginal ultrasonography, although quite effective for diagnosing ovarian cysts and tumors, is non-specific and its use for screening results in surgical exploration of a large number of women with benign ovarian cysts. The relative rarity of ovarian cancer, combined with the non-specific nature and relative sensitivity of currently available tests, makes ovarian cancer screening unsatisfactory.
The fate of surface-bound C3b depends entirely on the chemical nature of the surface allergy update purchase entocort in india. This enzyme is labile allergy shots ottawa order entocort 200 mcg online, but it is stabilized by the binding of P and is termed the amplification C3 convertase because it generates many C3b fragments and thus additional molecules of C3 convertase allergy forecast today buy entocort no prescription. Binding of a single C3b molecule to the C3 convertase gives rise to the (C3b)2 Bb complex allergy symptoms 11 order online entocort, Figure 271-2 Formation of complement convertases in the classic pathway of activation. The complement anaphylatoxins, C3a and C5a, react with specific receptors to stimulate the release of histamine from mast cells and basophils mediating smooth muscle contraction and increased vascular permeability. In the presence of interleukin-3 or interleukin-5, C5a also causes release of leukotrienes from basophils. In addition, C5a evokes neutrophil and monocyte responses, including up-regulation of cellular Figure 271-4 Formation of complement convertases in the alternative pathway of activation. When an activator is present, metastable C3b (C3b*) binds covalently to the activating surface and, because it is protected from the action of the regulatory proteins, initiates the assembly of the stable, amplification C3 convertase, which forms additional C3 convertase complexes and also the C5 convertase. The complex formed from the binding to C5b of one molecule of C6, C7, and C8 and of 1 to 12 molecules of C9 is termed membrane attack complex. It forms transmembrane pores by interacting directly with the lipid bilayer of biologic membranes. Collectively, the anaphylatoxins allow for the recruitment of host defense molecules and cells to tissue sites invaded by pathogens. C3b and its further cleavage fragments, C3bi and C3dg, react with multiple receptors distributed in a variety of cells (Table 271-2). This self-damaging potential of complement activation is normally kept under effective control by a number of inhibitors and inactivators that act at points of enzymatic amplification and also at the level of effector molecules. Certain of these proteins act as obligatory cofactors for the proteolytic enzyme I, which cleaves C4b and C3b into smaller fragments. With two exceptions, complement deficiencies are inherited as autosomal recessive traits. A rather limited number of clinical syndromes are associated with complement deficiencies. The underlying mechanisms are unclear, but impaired processing and clearance from the circulation of immune complexes and aberrant immunoregulation have been implicated in the pathogenesis of these syndromes. Deficiencies of C3, H, I, or P predispose to severe recurrent infections with encapsulated pyogenic bacteria. Lack of or inefficient opsonization of the bacteria by C3b/C3bi apparently causes the susceptibility to infection. Individuals deficient in C5, C6, C7, or C8 are susceptible to disseminated neisserial infection, most commonly meningococcal meningitis. Direct lysis by complement is probably required for effective defense against gonococci and meningococci. Individuals with C9 deficiency are usually less susceptible to neisserial infections. In certain human diseases, uncontrolled or aberrant activation of complement plays an important pathogenetic role. The classic pathway activated at tissue sites by autoantibodies against tissue antigens or by immune complexes deposited at basement membranes results in accumulation of inflammatory cells and tissue damage. Measurement of serum complement levels thus provides a simple and widely used tool to diagnose and manage certain human diseases. The most commonly used assays in clinical practice are total hemolytic complement, C4, and C3. In patients with partial lipodystrophy with or without glomerulonephritis and in some patients with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, levels of total complement and C3 are very low, whereas levels of C4 are usually normal. This is due to the presence of an IgG autoantibody, termed C3 nephritic factor, with specificity for the amplification C3 convertase. The alternative pathway is also activated during circulation of the blood through pump oxygenators or hemodialysis machines. The C5a generated during these procedures causes aggregation of neutrophils, leading to their sequestration in the pulmonary vasculature.
Cheap entocort 200mcg line. Asthma Attack in a child.
In fact allergy nurse salary discount entocort 200 mcg with amex, although "second-look" resections are now more commonly thought of in association with ovarian cancer allergy symptoms stiff joints order entocort amex, the procedure was first described in patients with colon cancer allergy testing vhi discount entocort 100mcg mastercard. Unfortunately allergy testing list order 200mcg entocort mastercard, the available evidence suggests that only a small percentage of patients are helped by this strategy. Patients in the latter category are most appropriately referred to a gynecologic oncologist who can perform a definitive procedure at the initial laparotomy. However, even in the latter group of patients, only about 50% of patients have a pathologic complete remission at the time of surgical re-exploration and approximately 50% of the patients with a pathologic complete remission will eventually relapse. However, as is the case with the use of other tumor markers, changes in treatment should not be considered on the basis of one measurement. They are not usually abnormal in early-stage disease, nor are they specific for breast cancer. Analogous to ovarian cancer, tumor markers play an even more important role in monitoring response to therapy in patients with disease that cannot be followed well by physical examination or with radiographic studies. For example, in patients with disease limited to bone, the bone scan may lag behind improvements in tumor marker levels by many months. Similarly, in patients with abdominal carcinomatosis, tumor marker measurements may substitute for more costly computed tomographies. An important caveat to the use of tumor markers in patients on hormonal therapy is that some patients will have a "flare" (worsening clinical disease and increase in tumor markers) weeks to months after beginning hormonal therapy. Because these patients predictably go on to have excellent responses, such patients should not have therapy changed prematurely. Nevertheless, because a variable number of cancers have been found by digital rectal examination alone, both tests are recommended by proponents of screening. Conversely, a great number of patients who do not have prostate cancer will be subjected to biopsies, thus increasing the cost of health care without any benefit. Nearly 50% of prostate cancers resected with curative intent are not confined to the prostate at the time of surgery. These data can theoretically be used to counsel patients before attempted definitive therapy with the anticipated result that fewer patients would opt for surgery in the face of a high chance of extra-organ tumor extension. Nevertheless, the most appropriate therapy for patients with early-stage prostate cancer by clinical criteria but with a high likelihood of extra-organ extension has not been defined. However, similar to the situation after surgery, a consensus on appropriate salvage treatment has not been reached. Androgen ablation therapy is the most effective treatment for patients with metastatic prostate cancer. This finding is particularly important because patients with metastatic prostate cancer generally do not have easily measurable disease. In patients with midline tumors (pineal, mediastinal, and retroperitoneum regions), markedly elevated germ cell markers are diagnostic of a testicular or extragonadal germ cell tumor and do not require biopsy for diagnosis. However, in view of the exquisite sensitivity of germ cell tumors to therapy, it is not unusual for patients to have a temporary rise in tumor markers early after chemotherapy, presumably owing to tumor cell necrosis, before a subsequent fall. If the tumor markers do not return to normal after chemotherapy, residual disease is almost invariably present. In patients with very high tumor markers at diagnosis, the tumor markers may not return to normal until 1 or 2 months after therapy is completed. However, nearly one third of patients with normal markers and residual masses will have residual disease. For a screening test to be effective, the disease in question must be relatively common, and efforts to detect early-stage 1042 disease must be focused in high-risk patients. In contrast, studies in Europe, where the prevalence of hepatoma is much lower and the majority of screened patients have cirrhosis unrelated to hepatitis infection, have not been particularly successful in detecting small and potentially resectable tumors. Importantly, because of the lower prevalence of hepatoma and more expensive testing in the United States, it has been estimated that the cost of detecting one hepatoma is as high as $270,000 compared with $8,000 in Japan. Multiple myeloma is a malignant lymphoproliferative disorder that is inevitably fatal in a period ranging from a few months to several years (see Chapter 181). Because of the extreme variability in the aggressiveness of disease even in patients who have the same clinical stage, it is helpful to identify patients with more aggressive disease who might benefit from experimental treatment, including bone marrow transplantation. Although a number of clinical and laboratory tests have been used to predict prognosis, at present the beta2 -microglobulin (beta2 -M) level is the most important (and generally available) prognostic factor in multiple myeloma. In a large cooperative group study, patients with a beta2 -M level less than 6 mug/mL had a median survival of 36 months compared with a median survival of 23 months in patients with a beta2 -M greater than 6 mug/mL. If serum albumin also was considered, patients could be divided into three prognostic groups.
Normally allergy medicine non drowsy purchase entocort 100 mcg free shipping, band neutrophils account for less than 4% of total circulating neutrophils allergy shots rush immunotherapy order entocort line. Band percentages greater than 6 to 7% suggest that the storage pool is releasing granulocytes early under the influence of increased levels of granulopoietic factors and suggests that neutrophils are being consumed in the periphery allergy testing galway entocort 100mcg on line. Alternatively allergy wheezing order on line entocort, if neutropenia is the result of bone marrow failure, the bone marrow may be in the midst of an early recovery. This risk of bacterial infection increases slightly as the peripheral neutrophil count falls below 1. Some patients with severe congenital neutropenia have such substantial compensatory monocytosis that their clinical course is very mild. Because of the capacity of the extra monocytes to "cover" for neutrophil deficiencies, such rare patients have few bacterial infections. Lungs, genitourinary system, gut, oropharynx, and skin are the most frequent sources of infection in neutropenic patients. The infecting organisms are the "usual suspects" for the given anatomic site with the caveat that, for patients who have recurrent infections and require prolonged and recurrent antibacterial therapy, unusual (often hospital-acquired) organisms can colonize and subsequently cause infection. Consequently, the antibiotic history of infected neutropenic patients is important to obtain. It is absolutely essential to recognize that the usual signs and symptoms of infection are often diminished or absent in patients with neutropenia because the cell that mediates much of the inflammatory responses to infection is absent. Thus, neutropenic patients with severe bilateral bacterial pneumonia can present, initially, with minimal infiltrates demonstrable on chest radiograph (sometimes no infiltrates at all until about 3 or 4 days of full-blown symptoms) and can have benign-looking, non-purulent sputum; patients with pyelonephritis may not exhibit pyuria; patients with bacterial pharyngitis may not have purulence in the oropharynx; and patients with severe bacterial infection of the skin may present only with some mild erythroderma rather than furunculosis. In the neutropenic patient, infections that in an otherwise normal individual might have been well localized become quickly disseminated. Therefore, not only is the infected neutropenic patient a diagnostic problem but, in addition, because any given infection is more likely to be widespread at the time of diagnosis, these patients are often gravely ill at the time they initially present to their caregivers. The diagnostic evaluation of neutropenia is influenced by its severity and the clinical setting in which it occurs. The patient with fever, sepsis, or both in whom neutropenia is discovered for the first time presents a particularly difficult problem. In such patients it is impossible to determine immediately whether the neutropenia antedated sepsis, a situation with both prognostic and therapeutic implications, or whether the neutropenia is merely a short-lived response to the infection itself. Examination of the peripheral blood smear and differential white blood cell count can be helpful in such cases. An increase in the fraction of circulating band neutrophil forms to levels above 20% suggests that marrow granulopoietic activity is responding appropriately. Although the clinical context is more important to consider than this single data point, colloquially known as "bandemia," it is, nonetheless, a data point more compatible with the notion that the bone marrow of the patient is in the midst of recovering from injury or that the neutropenia is derived from a transient shift to the marginated pool or to the extravascular compartment. The diagnostic evaluation of neutropenia must first address the question of the severity and then whether the patient has fever, sepsis, or both. The patient with sepsis and severe neutropenia should be treated promptly with intravenous antibiotics after obtaining appropriate cultures but without waiting for the results of those cultures. Once these important initial questions are answered, the remainder of the diagnostic evaluation can proceed. One is mediated by antineutrophil antibodies, the other by T lymphocyte-mediated bone marrow failure. After the severity of the neutropenia is determined, careful examination of the peripheral blood counts and blood smear is in order. Patients with selective neutropenia are approached differently than those with additional deficiencies of platelets and red cells, although drugs or toxins may be involved in either category. Potentially offending drugs should obviously be discontinued if such a maneuver is possible based on the nature of the disease for which the agent was prescribed and the availability of alternative drugs. Patients with selective neutropenia but with no drug or toxin exposure, no history of recurrent sepsis, and no underlying chronic inflammatory or autoimmune disease may have stable and benign neutropenia; this category includes some cases of familial and congenital neutropenia and pseudoneutropenia. Any patient with selective neutropenia with a history of sepsis and all patients with known toxin exposure should have a bone marrow examination to assess (1) the cellularity of each compartment (storage and mitotic pools), (2) the distribution of differentiation stages found in each pool, and (3) whether any morphologic abnormality.