"Buy 100 mcg cytotec amex, treatment kidney failure".
By: O. Kaelin, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, Idaho College of Osteopathic Medicine
For the online version of the book 8h9 treatment cheapest generic cytotec uk, it is suggested that you Barbara Illowsky & Susan Dean 7 medicine 369 purchase discount cytotec on-line. Starting cholesterol level 140 220 110 240 200 180 190 360 280 260 Ending cholesterol level 140 230 120 220 190 150 200 300 300 240 S 10 medications you can buy in mexico 200 mcg cytotec with mastercard. An experiment is conducted to show that blood pressure can be consciously reduced in people trained in a "biofeedback exercise program treatment dvt purchase cytotec 200mcg otc. The difference between blood pressures was calculated (after - before) producing the following results. She records their 18-hole scores before learning the technique and then after having taken her class. Player 1 Mean score before class Mean score after class 83 80 Player 2 78 80 Player 3 93 86 Player 4 87 86 the correct decision is: a. Southern States Alabama Arkansas Florida 2012 3,450 2,150 15,540 Barbara Illowsky & Susan Dean 7. The list of the cities with the corresponding hotel prices for his two favorite hotel chains is in Table. Cities Atlanta Boston Chicago Dallas Denver Indianapolis Los Angeles New York City Hyatt Regency prices in dollars 107 358 209 209 167 179 179 625 Barbara Illowsky & Susan Dean 7. Northeastern States Connecticut Delaware Maine Maryland Massachusetts New Hampshire New Jersey New York Ohio Pennsylvania Rhode Island Vermont West Virginia 2011 17. These problem categories include primarily (i) whether a data set fits a particular distribution, (ii) whether the distributions of two populations are the same, (iii) whether two events might be independent, and (iv) whether there is a different variability than expected within a population. The test statistic for a test of independence is similar to that of a goodness-of-fit test. The following bulleted list is a summary that will help you decide which Chi-square test is the appropriate one to use. You will now study a new distribution, one that is used to determine the answers to such questions. Figure: the chi-square distribution can be used to find relationships between two things, like grocery prices at different stores. The random variable for a chi-square distribution with degrees of freedom is the sum of independent, squared standard normal variables. Review the chi-square distribution is a useful tool for assessment in a series of problem categories. The random variable in the chi-square distribution is the sum of squares of df standard normal variables, which must be independent. The chi-square distribution curve is skewed to the right, and its shape depends on the degrees of freedom. Answer when the number of degrees of freedom is greater than 90 Is it more likely the df is 90, 20, or two in the graph The test statistic for a test of independence is similar to that of a goodness-of-fit test:) 1. If = y Let expected number of drivers who used a cell phone while driving and received speeding violations. Since the contingency table consists of two factors, the null hypothesis states that the factors are independent and the alternative hypothesis states that they are not independent (dependent). If we do a test of independence using the example, then the null hypothesis is:: Being a cell phone user while driving and receiving a speeding violation are independent events. The number of degrees of freedom for the test of independence is:) 1 - s w or f o rebmun 1 - snmu l oc f o rebmun(= fd Barbara Illowsky & Susan Dean 8. In a volunteer group, adults 21 and older volunteer from one to nine hours each week to spend time with a disabled senior citizen. The program recruits among community college students, four-year college students, and nonstudents. In Table is a sample of the adult volunteers and the number of hours they volunteer per week. Type of Volunteer Community College Students Four-Year College Students Nonstudents Column Total 1. Answer the observed table and the question at the end of the problem, "Is the number of hours volunteered independent of the type of volunteer
The other landmarks of the posterior hip and pelvis are mostly obscured by the great bulk of the gluteus maximus treatment zenker diverticulum discount cytotec 100mcg with mastercard, the principal extensor of the hip medications borderline personality disorder purchase cytotec 200mcg free shipping, which originates from the posterior portion of the iliac crest and inserts into both the fascia lata and the linea aspera of the posterior femur medicine 81 order cytotec 100mcg line. The area of the sacrum is visible as a triangular depression between the two great prominences created by the gluteus maximus muscles treatment goals and objectives buy cytotec 100 mcg on line. The sacrum tapers distally to the coccyx, which is palpable beneath the top of the midline crease of the buttocks. The ischium is the most inferior of the three bones that constitute the innominate, or pelvic, bone. Its inferior contour, the ischial tuberosity, constitutes the inferiormost portion of the pelvis. The ischial tuberosity is not normally visible, but it is palpable in the inferior medial buttock deep to the gluteus maximus. It serves as the origin for the hamstrings, the principal flexors of the knee, and a portion of the adductor magnus. Although the gluteus maximus obscures the deeper muscles of the posterior hip, their position can be estimated through knowledge of their relationship to the greater trochanter, whose prominence can usually be identified from the posterior perspective. A group of four short external rotators arises from the pelvis and inserts in a relatively small area on the superior portion of the greater trochanter. From superior to inferior they are the piriformis, the superior gemellus, the obturator interims, and the inferior gemellus. Tendinitis in these structures can be a source of posterior hip pain, and the piriformis is thought to sometimes compress the sciatic nerve, which emerges from beneath it. Two other transversely oriented muscles, the obturator externus and the quadratus femoris, insert further distally on the posterior margin of the greater trochanter. They are less likely than the external rotators to be implicated as a source of hip pain. The transverse crease that forms at the junction of the buttock and the posterior thigh is known as the gluteal Pelvis and Hip. Viewed from the lateral position, the most prominent landmark of the pelvis is the arching contour of the iliac crest. From the lateral perspective, the examiner is looking directly at the prominence created by the principal abductor of the hip, the gluteus medius. The gluteus medius arises from the superior portion of most of the iliac wing and inserts on the greater trochanter. Anterior to the gluteus medius, the tensor fascia lata arises from the most anterior portion of the iliac crest and constitutes the anterior border of the lateral aspect of the hip. Posterior to the gluteus medius, the bulky gluteus maximus muscle arises from the posterior ilium and adjacent sacrum. The belly of the gluteus maximus constitutes the familiar rounded contour of the buttock. Distal to the pelvic area, the vastus lateralis and the biceps femoris muscles constitute the anterior and the posterior contours of the thigh, respectively. The greater trochanter projects laterally to provide increased leverage for the gluteus medius and the gluteus minimus muscles that insert there. These critical muscles not only abduct the femur but also, more importantly, prevent drooping of the pelvis when the opposite limb is lifted from the ground during normal ambulation. These folds, which are formed as the gluteus maxinuis inserts into the posterior aspect of the proximal femur, are normally symmetric. Abnormalities of the hip, such as arthritis with hip joint subluxation or congenital hip dysplasia, cause the gluteal folds to appear asymmetric. The lateral margin of the posterior thigh is defined by the iliotibial tract. The visible muscle bulk consists primarily of the three hamstring muscles: the biceps femoris, the semimembranosus, and the semitendinosus. The biceps femoris, the sole lateral hamstring, originates from both the ischial tuberosity and the proximal femur and courses distally to a complex insertion on the fibular head.
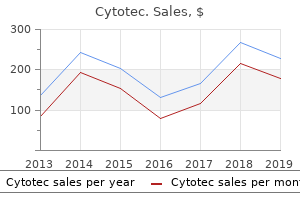
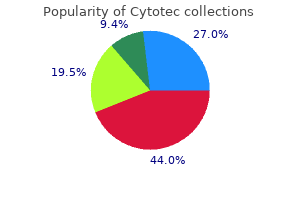
Buy cytotec 200 mcg lowest price. Excel and Questionnaires How to enter the data and create the charts YouTube.
This is usually due to an extensor mechanism problem treatment questionnaire discount 200 mcg cytotec with mastercard, such as quadriceps weakness or patellofemoral pain symptoms 0f diabetes cheap cytotec 100 mcg on-line. It should be remembered medicine engineering buy cytotec online, however medications cause erectile dysfunction discount cytotec 100mcg fast delivery, that patients with sciatica or tight hamstrings may also have difficulty fully extending the knee in the seated position. Complete inability to extend the knee against gravity suggests an extensor mechanism disruption such as a quadriceps tendon rupture, patellar fracture, or patellar tendon rupture. Normally, a patient should be able to get the heel close to the ipsilateral buttock, or even touching it. Measuring and comparing the heel-to-buttock distance is a good way to assess small amounts of loss of flexion. Loss of flexion is commonly due to effusion, arthritic change, or patellofemoral pain. Assessment of passive flexion is not always done because it is of limited clinical significance and may often produce pain. If passive flexion produces pain localized to one joint line, however, it may signify a tear of the respective meniscus. In this position, however, the obligate hip extension tightens the rectus femoris, which originates above the knee, and this may limit knee flexion to less than would be possible with the hip flexed. First, it allows the examiner to become oriented with the joint by identifying structures that are fairly superficial but not quite visible. This is particularly important in the presence of obesity or edema, when landmarks that might be visible in other patients are obscured. Finally, it may allow the examiner to make a presumptive diagnosis by documenting point tenderness on a specific anatomic structure. Any of the normal structures or abnormal prominences already described may be palpated for identification or to elicit tenderness. The areas of palpation described next are only those in which palpation is most commonly useful. However, it has been suggested that the lateral retinaculum itself may sometimes be the true source of pain. In the presence of the uncommon condition known as excessive lateral pressure syndrome, very little lateral play or glide is possible (see Patellofemoral joint in the Manipulation section). Careful palpation in this case reveals that tenderness is localized to the lateral patellofemoral ligament, a tight band about 1 cm wide connecting the lateral border of the patella to the lateral epicondyle. Anteromedial knee pain may occasionally be attributable to an inflamed medial patellar plica. This can sometimes be palpated as a palpable fibrous band running longitudinally between the patella and the medial femoral condyle. Flexion of the knee may tighten the plica over the medial femoral condyle and make it more prominent. Because the patella is such a frequent source of pain, its palpation should be part of virtually every knee examination. To elicit it, the examiner should ask the patient to lie supine with the legs fully extended and relaxed. If the quadriceps is adequately relaxed, it should feel flaccid and the patella should feel loose when the examiner shifts it from side to side. First, the examiner gently shifts the patella medially with one hand to expose as much of the medial facet as possible. While the patella is in this position, the index Finger or thumb of the other hand is worked under the medial facet as far as possible and pressed upward. Then the examiner reverses the process, shifting the patella laterally with one hand and palpating the exposed lateral facet with the other. Palpation of other portions of the extensor mechanism is indicated if the history or inspection raises the question of localized pathology. Figure 6-31 shows the common sites of tenderness in Osgood-Schlatter disease, Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease, patellar tendinitis, and quadriceps tendinitis. In the presence of quadriceps tendon rupture, the examiner may be able to palpate a gap as well as tenderness when the patient attempts to perform a straight-leg raise. Palpating the patellar tendon during an attempted straight-leg raise is also a good way to check for rupture of this structure. If the tendon is ruptured, it remains flaccid, and a gap, usually just distal to the patella, may be palpable.
When fully extended medications joint pain order cytotec from india, the normal fingers and thumb should hyperextend slightly symptoms diabetes buy cytotec in united states online, exhibiting a smooth medicine 95a cheap 100 mcg cytotec mastercard, gentle curve 6 mp treatment cheap cytotec 200 mcg. Avulsion of the insertion of the extensor digitorum communis from the dorsal base of the distal phalanx of one of the fingers is called a mallet finger. Just as wrist extension creates a flexor tenodesis and defines an arcade of bent finger position, flexion of the wrist causes all the finger to assume an extended position. Two classic deformities that are due to peripheral nerve injuries are benediction hand and claw hand. In this case, the proximal phalanx usually dislocates dorsally on the head of the corresponding metacarpal. In addition to the dorsal swelling created by the displacement of the proximal phalanx, a volar bulge may also be visible due to the prominence of the metacarpal head in the palm. Flexion deformities of the thumb and fingers may also be due to rupture of the relevant extensor tendon. Rupture of the extensor pollicis longus tendon at the wrist, the most common of these injuries, may occur following a fracture of the distal radius or may be due to rheumatoid synovitis. In the presence of extensor pollicis longus rupture, the patient has particular difficulty extending the intcrphalangeal joint of the thumb. These ruptures produce a flexion deformity of the involved metacarpophalangeal joints because the patient is still able to extend the interphalangeal joints using the intrinsic muscles of the hand. The extensor slip to the little finger is usually the first to rupture, followed progressively by the tendons to the ring, long, and index fingers over a variable period of time. This progressive series of extensor tendon ruptures is known as the VaughanJackson lesion. These tendons usually rupture with rheumatoid synovitis of the tendons and destruction of the carpal bones. The first tendon to rupture is the flexor pollicis longus; the ruptures then progress in an ulnar direction. This progressive series of flexor tendon ruptures is known as the Mannifelt lesion. After examining the extended fingers in pronation and supination for angular deformities, the finger alignment can be further assessed by asking the patient to supinate the hand and loosely flex the fingers together. The examiner begins by inspecting the fingertips end-on while the fingers are partly flexed. When viewed from this perspective, the flat of the nail of the index finger faces slightly away from that of the long finger while the nails of the ring finger and the little finger are slightly rotated in the opposite direction. Deviations from this alignment are most commonly due to rotational deformity following acute fracture or malunion of a phalangeal fracture. The examiner can further test the rotational alignment of the fingers and metacarpals by asking the patient to individually flex each of the four fingers toward the palm. When flexed as a group, they should stay in parallel alignment with each other. Rotational malalignment following an acute or malunited fracture of one of the metacarpals or phalanges causes the associated finger to deviate from the normal flexion alignment, possibly causing the adjacent fingers to diverge or cross (scissor) when they are flexed simultaneously. When fractures of the distal radius occur, the hand and distal radius are most commonly pushed dorsally. If this is incompletely reduced, the distal radius and hand remain dorsally displaced, resulting in a permanent step-off. Dislocations or fracture-dislocations at the radiocarpal or midcarpal joints can also produce step-off deformities, although the details may be quickly obscured by the dramatic swelling that can accompany such injuries. Loss of wrist motion is a common sequela of fractures or ligamentous injuries of or near the wrist. For measurement purposes, wrist motion is usually documented in four directions: flexion, extension, radial deviation, and ulnar deviation. During actual function, these motions can be combined in differing proportions, so that complete circumduction is possible.