"Order darunavir in united states online, medicine zithromax".
By: D. Reto, M.A.S., M.D.
Program Director, Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine
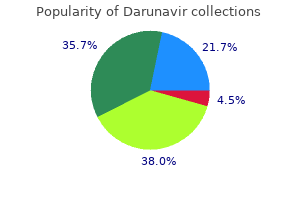
Patchy hair loss is often due to alopecia areata medications 101 discount 600 mg darunavir with amex, tinea capitis symptoms kidney stones best buy for darunavir, and trichotillomania medications you cant crush order 600 mg darunavir visa. Androgenetic alopecia may be diffuse or in a specific pattern medications you can take while pregnant for cold 600 mg darunavir free shipping, and may progress to complete baldness. Systemic symptoms such as fatigue and weight gain suggest hypothyroidism, whereas a febrile illness, stressful event, or recent pregnancy may account for the diffuse hair loss of telogen effluvium. The use of hair products such as straightening agents or certain shampoos suggests a diagnosis of trichorrhexis nodosa. A family history of hypothyroidism may warrant laboratory testing for this condition, whereas a family history of hair loss supports the diagnosis of androgenetic alopecia. Oral terbinafine (Lamisil), itraconazole (Sporanox), fluconazole (Diflucan), or griseofulvin is recommended for treatment of children with tinea capitis caused by Trichophyton infections. Cognitive behavior therapy is effective for the treatment of trichotillomania, and medical therapy may be more effective when combined with cognitive behavior therapy. The physical examination should focus on the hair and scalp, but attention should be given to physical signs of any comorbid disease indicated by the review of systems. If only the scalp is involved, the physician should look for typical male or female pattern to determine the presence of androgenetic alopecia. Dry, broken hair suggests trichorrhexis nodosa, whereas scaling, pustules, crusts, erosions, or erythema and local adenopathy suggest infection. Summary of Nonscarring Alopecia Type Alopecia areata Significant features Acute, patchy hair loss; examination shows short, vellus hairs, yellow or black dots, and broken hair shafts Diffuse hair loss days to weeks after exposure to a chemotherapeutic agent; incidence after chemotherapy is estimated at 65% Family history of hair loss; gradually progressive course Men: bitemporal thinning of the frontal and vertex scalp, complete hair loss with some hair at the occiput and temporal fringes Women: diffuse hair thinning of the vertex with sparing of the frontal hairline Telogen effluvium Clumps of hair come out in the shower or in hairbrush; associated with physiologic or emotional stress Treatment and comments Intralesional triamcinolone acetonide injected intradermally High rate of spontaneous remission No pharmacologic intervention has been proven effective; scalp cooling not recommended Minoxidil may help during regrowth period Men: topical minoxidil (2% or 5% solution) Women: topical minoxidil (2% solution) Treatment should continue indefinitely because hair loss reoccurs when treatment is discontinued Adverse effects include hypertrichosis (excessive hair growth for age, sex, and race) and irritant or contact dermatitis Treatment involves removing the underlying cause and providing reassurance Condition is usually self-limited and resolves within two to six months Requires systemic treatment because topical antifungals do not penetrate hair follicles Trichophyton species: oral terbinafine (Lamisil), itraconazole (Sporanox), fluconazole (Diflucan), or griseofulvin Microsporum species: griseofulvin Trichorrhexis nodosa Hairs break secondary to trauma or because of fragile hair (congenital or genetic); causative traumas include excessive brushing, heat application, hairstyles that pull on hairs, and conditions that cause excessive scalp scratching Patches of alopecia, typically frontoparietal, that progress backward and may include the eyelashes and eyebrows Stop offending actions Anagen effluvium Androgenetic alopecia Tinea capitis Dermatophyte infection of the hair shaft and follicles; patients present with patchy alopecia with or without scaling Trichotillomania Optimal treatment is unknown; strong evidence is lacking for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; cognitive behavior therapy with habit reversal and medications may be more effective than either approach alone Psychiatric referral may be indicated 372 American Family Physician A positive result is when more than 10% of hairs (four to six) are pulled from the scalp; this implies active hair shedding and suggests a diagnosis of telogen effluvium, anagen effluvium, or alopecia areata. The pull test is difficult to standardize because the pulling force is not distributed uniformly and because it is difficult to approximate the number of hairs grasped, thereby leading to false interpretations. Laboratory testing is indicated when the history or physical examination findings suggest an underlying comorbidity. Common Findings, Related Diagnoses, and Workup for Hair Loss Common findings Abrupt onset of hair loss Gradual onset of hair loss Related diagnosis Telogen effluvium related to a specific event Alopecia areata Diagnostic workup and comments Inquire about inciting event History and physical examination findings are diagnostic Pull test: increased telogen-to-anagen ratio (greater than the normal ratio of 1:10) Androgenetic alopecia Scarring alopecias Diffuse hair loss Alopecia totalis if more than scalp is involved Systemic disease. It is most prevalent in white men, with 30%, 40%, and 50% experiencing androgenetic alopecia at 30, 40, and 50 years of age, respectively 2 (Figure 1). Although this condition is less common in women, 38% of women older than 70 years may be affected3 (Figure 2 4). Men typically present with bitemporal thinning, thinning of the frontal and vertex scalp, or complete hair loss with residual hair at the occiput and temporal fringes. Common conditions that mimic androgenetic alopecia include thyroid disease, iron deficiency anemia, and malnutrition. Topical minoxidil (2% or 5% solution) is approved for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in men. Hair regrowth is more robust at the vertex than in the frontal area, and will take six to 12 months to improve. Minoxidil 2% solution is recommended for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women. Finasteride (Propecia), 1 mg per day orally, is approved to treat androgenetic alopecia in men for whom topical minoxidil has been ineffective. Adverse effects of finasteride include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and gynecomastia. Both of these drugs stimulate hair regrowth in some men, but are more effective in preventing progression of hair loss. Although there are a number of other treatments listed in various 374 American Family Physician The diagnosis can Volume 96, Number 6 September 15, 2017 Hair Loss Distal shaft (normal caliber) Proximal shaft (thinned) Figure 5. Exclamation point hair showing distal broken end of shaft and proximal clubshaped hair root. Other therapies for the treatment of alopecia areata include topical mid- to high-potency corticosteroids, minoxidil, anthralin, immunotherapy (diphenylcyclopropenone, squaric acid dibutylester), and systemic corticosteroids. Hair loss in alopecia areata occurs in three different patterns: patchy alopecia is circumscribed, oval-shaped, flesh-colored patches on any part of the body; alopecia totalis involves the entire scalp; and alopecia universalis involves the whole body. Evaluation of the scalp may reveal short vellus hairs, yellow or black dots, and broken hair shafts (which are not specific to alopecia areata). Microscopic examination of the hair follicles demonstrates exclamation mark hair.
This new estimate is not very different from 1 Gy that has been used thus far and was based entirely on mouse data medications zovirax buy generic darunavir canada. The conceptual basis and the database used for estimating the average spontaneous and induced rates of mutations medications definition buy cheap darunavir 600mg on-line, however medicine woman generic 600 mg darunavir with amex, are now different symptoms of pneumonia buy cheapest darunavir. It is worth reiterating here that this is the first time an attempt has been made to use the mutation data coming not only from the 7 specific loci but also from all loci for which there are published data (a total of 34 loci; see Table 4-3C) taking into account interlaboratory and interexperimental variations in induced rates. Unfortunately, all of the data from biochemical loci and for dominant visibles were from Let P be the disease prevalence before an increase in mutation rate and P its change due to a m change in spontaneous mutation rate, m. In this equation, since P/P is the relative change in disease prevalence and m/m is the Copyright National Academy of Sciences. Because of the paucity of human data, until recently, estimates of m/m have been obtained from mouse data and assumed to be applicable to the human situation. Note that despite the different notations used, Equation (4-4) is the same as the Equation (4-3), the basic risk equation. The HardyWeinberg concept thus summarizes the basic characteristic of stability of allele frequencies (and therefore of genotype frequencies) over time in large, randomly breeding populations in the absence of differences in viability or fertility among the genotypes, migration, mutation, and geographical subdivision of the population. In the case of genetic diseases, this is reflected as their stable prevalences in the population. With more than two alleles, the extension is straightforward: the binomial expansion becomes multinomial (Crow 2001). Mutation-Selection Balance Spontaneous mutations arise in each generation at a finite rate, and most are eliminated sooner or later by natural selection. At equilibrium, the rate of origin of new alleles by spontaneous mutation will be equal to the rate at which they are eliminated by selection and is called the mutation-selection equilibrium. The equilibrium frequency of the mutant allele depends on whether that allele is recessive or dominant. In a stable gene pool, with the allele a mutating to A at a rate of m per generation, ignoring back mutations, there will be an mq amount of new disease-causing mutant alleles per generation; this will be counterbalanced by an elimination of these alleles by selection, which amounts to pqs + p2s. At equilibrium, these two quantities should be equal, yielding an equilibrium allele ^ frequency of A. The first of these relates the frequencies of mutant alleles to those of genotypes in large randomly mating populations, and the second describes the dynamics of mutant genes in populations. If the parents mate at random, which is equivalent to combining genes at random from a large pool to which each parent has contributed equally, the zygotes are in Hardy-Weinberg proportions. The larger the population, the closer the num- because the mutation rate (m) is generally smaller than the selection coefficient (s). At low mutant allele frequencies, the frequency of dominant diseases at equilibrium is then ^ ^^ ^ predicted to be p 2 + 2 pq 2 p. The starting assumption in these computations is that the population is in mutation-selection equilibrium prior to radiation exposure. When the population sustains radiation exposure, the mutation rate is increased, which in turn will impact disease frequency. If, on the other hand, the population is exposed to radiation generation after generation. With a permanent doubling of the mutation rate, for the selection coefficient of 0. For example, about 40% of retinoblastoma cases are due to germline mutations and the remaining ones are sporadic (Vogel 1979). For such diseases, the disease frequency at equilibrium can be assumed to take the form P = A + Bm. With A (sporadic component) and B (germinal component) as constants, only the second term will be responsive to an increase in mutation rate.
Cognitive and other adverse e ects of diphenhydramine use in hospitalized older patients medications kidney patients should avoid purchase darunavir 600mg mastercard. Measuring the su ering of end-stage dementia: reliability and validity of the Mini Su ering State Examination medicine 3601 buy darunavir with a mastercard. Diagnostic and treatment guidelines on elder abuse and neglect [American Medical Association] symptoms electrolyte imbalance generic 600 mg darunavir with mastercard. E ectiveness of nonpharmacological interventions for the management of neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with dementia medications similar to abilify cheap darunavir 600 mg visa. E ective behavioral interventions for decreasing dementia-related challenging behaviors in nursing homes. Avoiding family feuds: Responding to surrogate demands for life-sustaining interventions. Survival of a cohort of elderly patients with advanced dementia: nasogastric tube feeding as a risk factor for mortality. Eating behavior in persons with moderate to late-stage dementia: Assessment and interventions. Aromatherapy as a safe and e ective treatment for the management of agitation in severe dementia: the results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with Melissa. Depressive symptomatology and incident cognitive decline in an elderly community sample. Dementia assessment in primary care: Results from a study in three managed care systems. Factors relating to the use of physical restraints in psychogeriatric care: a paradigm for elder abuse. What is the moral authority of family members to act as surrogates for incompetent patients A randomized placebo-controlled trial of risperidone for the treatment of aggression, agitation, and psychosis of dementia. Meta-analysis of psychosocial interventions for caregivers of people with dementia. Medication use leading to emergency department visits for adverse drug events in older adults. Recreation clubs: an outcomebased alternative to daycare for older adults with memory loss. E ects of physician communication style on client medication beliefs and adherence with antidepressant treatment. Enhancing the quality of life of dementia caregivers from di erent ethnic or racial groups: A randomized, controlled trial. Using a new taxonomy to combine the uncombinable: integrating results across diverse interventions. Cultural diversity in Alzheimer disease: e interface between biology, belief, and behavior. Nonpharmacologic interventions for inappropriate behaviors in dementia: a review, summary, and critique. Longitudinal changes in behavior problems in old age: A study in an adult day services population. E ectiveness of collaborative care for older adults with Alzheimer Disease in primary care: A randomized controlled trial. A systematic review of the e cacy and safety of atypical antipsychotics in patients with psychological and behavioral symptoms of dementia. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. Anticholinergic di erences among patients receiving standard clinical doses of olanzapine or clozapine. Behavioral e ects of memantine in Alzheimer disease patients receiving donepezil treatment. Patients and families desire a patient to be told the diagnosis of dementia: a survey by questionnaire on a Dutch memory clinic.
Syndromes
- Dizziness
- The amount of time you spend on a waiting list is usually not a factor in how soon you get a liver, with the possible exception of children.
- Sarcoidosis
- Cough
- Feeding problems
- Problem keeps coming back (recurrence)
After exposure to a dose of radiation treatment statistics order darunavir without a prescription, there typically is a delay of several years (the latent period) before any cancer is observed treatment trends buy darunavir. A table showing the number of persons who symptoms ketoacidosis buy cheap darunavir online, of a given number born or living at a specified age treatment uterine fibroids buy darunavir 600mg amex, live to attain successivly higher ages, together with the numbers who die in each interval. The combined effect of two agents is equal to the product of the effects of the two agents acting alone. Council commissioned to formulate and disseminate information, guidance, and recommendations on radiation protection and measurements. Any new and abnormal growth, such as a tumor; neoplastic disease refers to any disease that forms tumors, whether malignant or benign. A description of effects whose severity is a function of dose; for these, a threshold may occur; some examples of somatic effects believed to be nonstochastic are cataract induction, nonmalignant damage to the skin, hematological deficiencies, and impairment of fertility. The so-called bell-shaped curve of randomly distributed quantities; also referred to as a "Gaussian distribution. The odds of being exposed among diseased persons divided by the odds of being exposed among nondiseased persons. The genetically and environmentally determined physical appearance of an organism. An electromagnetic quantum whose energy (Eph) equals the product of the Planck constant (h) and its frequency (n). An analysis of epidemiologic data from several studies based on original data from the studies. The number of cases of a disease in existence at a given time per unit of population, usually 100,000 persons. A number that expresses the probability that a given cancer, in a specific tissue, has been caused by a previous exposure to a carcinogenic agent, such as radiation. A mathematical model that simultaneously describes the excess cancer risk at different levels of some factor such as dose, time after exposure, or baseline level of risk, in terms of a parametric function of that factor. It becomes a projection model when data in a particular range of observations are used to assign values to the parameters in order to estimate (or project) excess risk for factor values outside that range. An agent that is not by itself carcinogenic but can amplify the effect of a true carcinogen by increasing the probability of late-stage cellular changes necessary to complete the carcinogenic process. The ratio of the percentage of a specific cause of death among all deaths in the population being studied divided by the comparable percentage in a standard population. The spreading out of a radiation dose over time by continuous delivery at a lower dose rate. A model that assumes that the excess risk is proportional to the square of the dose. Energy emitted in the form of waves or particles by radioactive atoms as a result of radioactive decay or produced by artificial means, such as X-ray generators. The property of nuclide decay in which particles or gamma radiations are usually emitted. Man-made radioactivity produced by fission, fusion, particle bombardment, or electromagnetic irradiation. The property of radioactivity exhibited by more than 50 naturally occurring radionuclides. A radioactive atomic species of an element with the same atomic number and usually identical chemical properties. A radioactive species of an atom characterized by the constitution of its nucleus. The ratio Dref/D, where D is the absorbed dose of a specified radiation and Dref is the absorbed dose of a sparsely ionizing reference radiation (-rays or X-rays) that produces the same level of effect. The rate of disease in an exposed population divided by the rate of disease in an unexposed population. Increased effectiveness results from an interaction between two agents, so that the total effect is greater than the sum of the effects of the two agents acting alone. Cells in a tissue that have been determined to be the key cells in which changes occur in order to produce an end point such as cancer. Tissue culture cells changed from growing in an orderly pattern exhibiting contact inhibition to growing in a pattern more like that of cancer cells.
600mg darunavir mastercard. Warning Signs Of Dehydration | 6 Signs That You Are Not Drinking Enough Water.