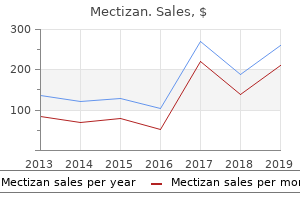
"Order mectizan overnight delivery, treatment for uti guidelines".
By: S. Giacomo, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Professor, Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine
There may be difficulty with expression as the individual may not know what is considered appropriate or inappropriate behavior should i use antibiotics for sinus infection buy mectizan 3 mg overnight delivery. Issues related to time and place bacterial pneumonia order 3 mg mectizan with amex, unacceptable social contact antibiotics dizziness generic 3 mg mectizan with visa, or problems with privacy are common bacteria yogurt lab mectizan 3mg with amex. They may have difficulty with activities of daily living such as buttoning, zipping or snapping. Decreased or increased muscle tone may be present making performance of everyday activities difficult. Motor planning may also be impacted resulting in problems executing steps to a motor activity such as kicking a ball or tying a shoe. For students with motor difficulties, it is often necessary to elicit the services of an occupational therapist. Instructional Focus Areas: V Gross motor j Demonstrate motor control j Sit with stability j Balance j Demonstrate appropriate physical strength j Demonstrate locomotion skills j Perform motor activities. Common are atypical patterns of attending and failure to receive relevant information. Processing systems may not function instantaneously and automatically resulting in a lack of organization or analysis of this information. Students will likely have difficulty with abstract concepts and nuances and have a greater ability to learn material by rote than by symbolism and analogy (Anzalone & Williamson, 2000). Deficits in components related to executive functioning impact ability to organize, problem solve, and plan for future behavior (Lopez, Lincoln, Ozonoff, & Lai, 2005). Instructional Focus Areas: V Attending j Sustain attention j Attend to relevant information or cues j Shift attention V 22 V Virginia Department of Education, Office of Special Education and Student Services Models of Best Practice in the Education of Students with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Preschool and Elementary V May 2011 j j j j j j j Categorize relationships Categorize social interactions Categorize ideas Create categories Extend concepts to similar items Describe similarities and differences Understand value, importance, and significance j Understand nuance and gradation j Determine the nature of the category. Instructional Focus Areas: V English j Demonstrate skills related to reading G Identify letters and letter sounds G Use phonics to read and spell G Read with fluency and expression G Expand vocabulary comprehension G Comprehend fiction and nonfiction reading material G Ask and answer who, what, when, where, why, and how questions G Identify characters, setting, and important events G Retell stories and events using beginning, middle, and end G Make predictions G Identify topic or main idea G Organize information and events logically G Make connections between previous experiences and reading selections G Draw conclusions G Summarize major points G Identify cause and effect G Compare-and-contrast relationships j Demonstrate skills related to writing G Write letters and numbers G Write words G Write sentences G Develop ideas Academic Performance Characteristics of Academic Performance: Academic performance, for this discussion, refers to tasks related to the core content areas of English, mathematics, science, and history/social science. Impairment in cognition coupled with Virginia Department of Education, Office of Special Education and Student Services V 23 V Models of Best Practice in the Education of Students with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Preschool and Elementary V May 2011 G G G G G G G Sequence thoughts and organize writing Use appropriate language and descriptive vocabulary Apply grade level writing conventions. Differences in sensory processing can be confusing and have a pervasive effect (Whitman, 2004). Oversensitivity and/or undersensitivity to sensory input results in patterns of behavior which detract from learning experiences. When the sensory processing systems are working correctly, the person is able to take in information from the environment, organize it, make sense of it and execute a response automatically. When they are not functioning appropriately, there may be interference, distractions, and difficulty with behavior. Educational placement decisions must be based on the assessed strengths, challenges, and educational needs of the student rather than on the label of autism. Placement options range from total inclusive settings where students receive their education alongside nondisabled peers to private placement in residential programs for individuals with disabilities. Within that range, a wide variety of plans can be created to meet the distinct needs of each student. Using the continuum concept makes it more likely that each student will be placed appropriately in an environment that is specifically suited for him or her. Restricted and Repetitive Patterns of Behavior Characteristics of Restrictive and Repetitive Behaviors: Unusual and distinctive patterns of behaviors may be demonstrated, including preoccupation with objects or parts of objects, intense interest in specific topics, or an intense need for sameness. Students may engage in stereotyped, or repetitive motor movements, which commonly manifest as finger flicking, hand flapping, unusual eye gazing, or spinning. Stereotypies can interfere with learning new behaviors and perseverations may limit motivation. Many of the restricted and repetitive behaviors may be caused by a number of different factors, such as sensory processing, difficulties in understanding social situations, limited play skills, and anxiety (Lopez, Lincoln, Ozonoff, & Lai, 2005). When planning instruction, educators need to consider the behavior and its function for that individual student and develop a plan accordingly. Successful teaching strategies should focus on making environmental adaptations to decrease interfering behavior and help the student learn other more appropriate behaviors that will serve the same function. This requires a flexible model that is able to address the individual needs of these students.
Diseases
- Sutton disease II
- Chanarin disease
- Muscular dystrophy congenital, merosin negative
- Chromosome 3, monosomy 3q21 23
- Pseudoxanthoma elasticum, dominant form
- Melhem Fahl syndrome
Alcohol inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis and can provoke treatment for dogs chewing paws discount mectizan express, prolong or exacerbate hypoglycemia virus x the movie best order for mectizan. They also decrease certain catecholaminemediated symptomatic and metabolic responses to hypoglycemia; awareness of hypoglycemia may therefore be reduced antibiotics in animals cheap mectizan 3 mg overnight delivery, and recovery of normoglycemia delayed antibiotic resistance hospital acquired infections purchase mectizan online. These adverse effects are much less pronounced with cardioselective 1-adrenoceptor antagonists. Metformin and several sulfonylureas are cleared through the kidney; they are therefore contraindicated in advanced nephropathy and should not be co-administered with nephrotoxic drugs. This chapter discusses the problems posed by drug therapy in the management of people with diabetes. Numerous drugs can affect diabetic control, causing hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia, by interfering with insulin secretion or action or both, or by interacting with antidiabetic agents. The special considerations that apply when using other drugs in patients with diabetes and in the presence of specific diabetic complications are also discussed. Drugs that raise blood glucose concentrations Drug-induced diabetes is now recognized as a distinct etiologic category, and diabetogenic drugs are discussed in detail in Chapter 16. Most of these drugs notably glucocorticoids (a common and important cause of iatrogenic diabetes), contraceptive steroids and adrenoceptor antagonists act by inhibiting insulin action. By contrast, insulin secretion is inhibited by diazoxide, while pentamidine can cause permanent -cell damage. These are now widely used by people with diabetes up to onethird of patients in one study [11] and some products may contain naturally occurring or synthetic glucose-lowering agents (Table 26. Drugs that lower blood glucose concentration Sulfonylureas Many drugs can cause hypoglycemia (Table 26. These include some that interact with and enhance the action of glucose-lowering drugs. Others act in their own right as insulin secretagogues, or to enhance or mimic the effect of insulin in suppressing glucose production by the liver and stimulating glucose uptake into peripheral tissues. Drugs should always be suspected whenever patients with previously well-controlled diabetes experience unexplained hypoglycemic episodes, or if dosages of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents decline. As well as prescription drugs, patients should be asked about herbal, traditional and other alternative medicines. Sulfonylureas are an important and sometimes unrecognized cause of symptomatic hypoglycemia (see Chapter 33). The long-acting sulfonylureas glibenclamide and chlorpropamide are especially troublesome. In one outpatient survey, 20% of patients treated with glibenclamide reported symptoms of hypoglycemia within the previous six months [12], while other surveys suggest that tolbutamide is much less likely to cause severe hypoglycemia. A Swiss study [15] defined the risk of severe hypoglycemia as two episodes per 1000 persons per year in those given glibenclamide, over twice as high as in those taking shorter-acting sulfonylureas such as tolbutamide, gliclazide or glipizide. The novel sulfonylurea, glimepir- 411 Part 5 Managing the Patient with Diabetes Table 26. None the less, the rate of hypoglycemia is still substantial, with 1020% of patients experiencing at least one mild episode each year [16]. Several factors other than the individual drug per se can increase the risk of hypoglycemia from sulfonylureas, notably increasing age and renal impairment [13,14,1618]. Sulfonylurea-induced hypoglycemia can be profound and prolonged, and difficult to manage. Patients with sulfonylureainduced hypoglycemia may require admission and treatment with glucose until the effect of the sulfonylurea has worn off although caution is needed as indicated in the case report below. Case report: Severe relapsing sulfonylurea-induced hypoglycemia A 62-year-old woman was admitted with acute confusion and became unresponsive 2 hours after admission. She had type 2 diabetes with impaired renal function (serum creatinine 176 mol/L) and had been taking 40 mg gliclazide twice a day. The hypoglycemia was reversed with an intravenous bolus of 50 mL 50% glucose but subsequently she had repeated episodes of hypoglycemia and required continuous intravenous glucose infusion for 3 days.
3mg mectizan mastercard. Producer REAGIERT auf SUPER JUNIOR 슈퍼주니어 'SUPER Clap' MV.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and angiotensin-(1-7): an evolving story in cardiovascular regulation antibiotics for pneumonia buy 3 mg mectizan with visa. Prevention of accelerated atherosclerosis by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in diabetic apolipoprotein E-deficient mice antibiotics yom kippur buy mectizan 3 mg without prescription. Effects of candesartan on the development of a new diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in patients with heart failure virus 4 fun order mectizan 3mg amex. Risk of new-onset diabetes in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study bacteria joint pain order mectizan 3mg with mastercard. Release of nitric oxide by angiotensin-(1-7) from porcine coronary endothelium: implications for a novel angiotensin receptor. Angiotensin-(1-7) dilates canine coronary arteries through kinins and nitric oxide. Angiotensin-(1-7) antagonist A-779 attenuates the potentiation of bradykinin by captopril in rats. The renin-angiotensin system in a rat model of hepatic fibrosis: evidence for a protective role of angiotensin-(1-7). Rosiglitazone attenuates atherosclerosis in a model of insulin insufficiency independent of its metabolic effects. Lack of the antioxidant enzyme glutathione peroxidase-1 accelerates atherosclerosis in diabetic apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Site-specific antiatherogenic effect of the antioxidant ebselen in the diabetic apolipoprotein E-deficient mouse. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition with quinapril improves endothelial vasomotor dysfunction in patients with coronary artery disease. Improvement in endothelial function by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Losartan, an angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonist, improves endothelial function in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Effects of the angiotensin-receptor blocker telmisartan on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients intolerant to angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors: a randomised controlled trial. Influence of noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus on plasma endothelin-1 levels in patients with advanced atherosclerosis. Carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 654 Pathogenesis of Macrovascular Complications Chapter 39 mellitus: potential role of endothelin-1, lipoperoxides, and prostacyclin. Role for nuclear factor-B and signal transducer and activator of transcription 1/interferon regulatory factor-1 in cytokineinduced endothelin-1 release in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Human monocyte adhesion is modulated by endothelin B receptor-coupled nitric oxide release. Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Systemic tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand delivery shows antiatherosclerotic activity in apolipoprotein E-null diabetic mice. Osteoprotegerin inactivation accelerates advanced atherosclerotic lesion progression and calcification in older ApoE-/- mice. Immunological characterization of circulating osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor: increased serum concentrations in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Osteoprotegerin gene polymorphism and the risk of osteoporosis and vascular disease. Increased plasma concentrations of osteoprotegerin in type 2 diabetic patients with microvascular complications. Association between mannose-binding lectin and vascular complications in type 1 diabetes. Increased levels of mannan-binding lectin in type 1 diabetic patients with incipient and overt nephropathy. Terminal complement blockade with pexelizumab during coronary artery bypass graft surgery requiring cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized trial. The effect of nisoldipine as compared with enalapril on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes and hypertension.
Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (Edta). Mectizan.
- Hardened skin (scleroderma).
- What other names is Edta known by?
- Emergency treatment of life-threatening high calcium levels (hypercalcemia).Treating heart rhythm problems caused by drugs such as digoxin (Lanoxin).
- Dosing considerations for Edta.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Edta work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Treating corneal (eye) calcium deposits.
- What is Edta?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96988