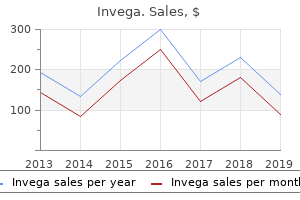
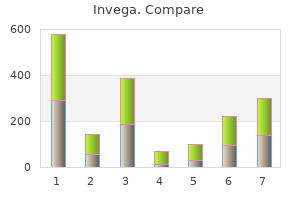
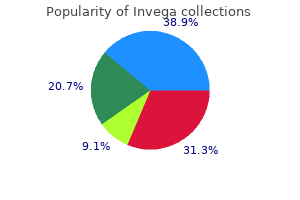
"Invega 3mg visa, medications for bipolar".
By: G. Abe, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Program Director, California Northstate University College of Medicine
Preservative-free preparation is used intracamerally during an intraocular surgery medicine joji order invega now. Methylcellulose (Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose 2%) is mainly viscous and barely elastic treatment wasp stings cheap invega online mastercard. Chondroitin sulfate is a natural compound of connective tissue and is less elastic than sodium hyaluronate treatment carpal tunnel generic invega 3mg with amex. Phacoemulsification: the viscoelastic substances are used to protect the corneal endothelium 247 medications invega 6mg for sale, create more space by deepening the anterior chamber, dilate a poorly dilating pupil, tear the lens capsule during capsulorhexis and push the iris back in case of positive vitreous thrust during phacoemulsification. The use of viscoelastic substances is not totally free from side effects, postoperative transient rise in intraocular pressure is frequently encountered. Therefore, removal of viscoelastic material after completion of surgery through irrigation-aspiration is recommended. Considering the cost involvement and side effects, some eye surgeons prevents excessive postoperative scarring. Corneal epithelial erosion and wound leak are common complications of this antifibrosis agent. Mitomycin-augmented surgery prevents excessive postoperative scarring and, hence, reduces the risk of failure of filtering surgery or recurrence of pterygium. Ideally, a viscoelastic substance should be inert, crystal clear, hydrophilic, elastic and viscous. Its viscosity creates space (deep anterior chamber or capsular bag distention) even under positive pressure and facilitates intraocular maneuvers safely. Streptomycin Symptom Sign Photophobia, central scotoma, visual loss Visual impairment, scotoma Scotoma, loss of vision Disturbance in vision especially for near, scotoma Visual impairment, swelling of the eye, central scotoma Visual disturbance, scotoma, difficulty in near work Headache, visual impairment Photophobia, xanthopsia, scotoma, poor night vision, defective color vision, diplopia, hallucination Scintillating scotoma, dryness of eyes Poor night vision, color vision defect, diplopia Redness of eyes, dryness of eye, color vision defects Swelling of lids Visual disturbances, scintillating scotoma, diplopia, contact lens intolerance Diplopia, blurred vision 2. A Nystagmus, hyphema, keratitis, mydriasis, papilledema, toxic amblyopia Retinal pigmentation, retinal edema, papilledema, toxic amblyopia Conjunctival injection, corneal vascularization, retinal hemorrhages, toxic amblyopia Lid edema, optic neuritis, toxic amblyopia Myopia, nystagmus, corneal edema, occlusion of central retinal vein and artery, papilledema (intracranial hypertension) Nystagmus, exophthalmos, retinal hemorrhages, papilledema (intracranial hypertension) Contd. Some of the systemic drugs when administered for the treatment of extraocular disorders cause adverse ocular effects. Therefore, a general physician should know the ocular toxicity of commonly prescribed drugs. Important side effects of commonly used systemic drugs are listed in the Table 10. The marginal conjunctiva forms a transitional zone between the skin of the lid and the conjunctiva proper. It is continuous for about 2 mm on the back of the lid forming the subtarsal fold. The tarsal conjunctiva is firmly adherent to the tarsus of the upper lid, while in the lower lid it is only adherent to the breadth of the tarsus. The orbital part of the conjunctiva lies loosely between the upper border of the tarsal plate and the fornix. It is freely movable over the sclera excepting a zone of 3 mm width around the cornea (limbal conjunctiva) and at the insertions of the rectus muscle tendons. The limbus is a circular transitional zone between the cornea on one hand and the conjunctiva and the sclera on the other. It shows papilliform digitations and contains blood vessels, lymphatics and melanin pigments. The forniceal conjunctiva is a continuous culde-sac which is interrupted on the medial side by the caruncle and plica. The conjunctiva is a translucent membrane which covers the posterior surface of the lids and then reflected onto the anterior part of the eyeball upto the margin of the cornea (limbus). It has 3 parts: the palpebral conjunctiva lining the eyelid, the bulbar conjunctiva covering a part of the eyeball and the fornix which unites the two. The adenoid layer consists of loose connective tissue containing lymphocytes, mast cells and histiocytes. The adenoid layer does not develop until after the first 2 or 3 months of life, hence, follicles do not appear in early infancy. Goblet cells, serous glands and accessory serous glands are found in the conjunctiva. Numerous mucus secreting goblet cells are present in the epithelium of bulbar conjunctiva and fornix. They are true unicellular mucous glands which moisten the conjunctiva and the cornea by discharging mucin.
The conjunctival veins drain either in the posttarsal venous plexus of the lid or in the superior or inferior ophthalmic vein medicine urology buy invega online pills. Lymphatics of conjunctiva lie superficially as well as deep and form an irregular network treatment non hodgkins lymphoma purchase invega 6 mg line. The lymph vessels from the lateral side drain into the preauricular lymph nodes and those from the medial side into the submandibular nodes medicine youth lyrics 6 mg invega with visa. Nerve Supply of the Conjunctiva the sensory nerve supply of the conjunctiva is derived from the trigeminal nerve-from the infratrochlear branch of nasociliary nerve medications 25 mg 50 mg order invega online from canada, supratrochlear and supraorbital branches from the frontal nerve, the lacrimal nerve and the infraorbital nerve. The sympathetic nerves come from the sympathetic plexus along the branches of the ophthalmic artery. The palpebral conjunctiva is supplied by the post-tarsal plexus of the upper and lower lids. The perforating branches from the peripheral palpebral arcade supply the fornix, their descending branches anastomose with the marginal Bacterial Flora of the Conjunctiva the conjunctiva is practically never free from organisms. Propionibacterium acnes and Corynebacterium xerosis can be isolated from the healthy conjunctiva. A relatively low temperature of the conjunctiva due to constant evaporation of tears, mecha- Diseases of the Conjunctiva 111 nical action of the lids, pumping action on the tear drainage system, constant epithelial exfoliation and a moderate blood supply make the conjunctiva unsuitable for the propagation of organisms. Further, tears contain lysozymes, betalysins, IgA and IgG, all of which inhibit bacterial growth. Nevertheless, the conjunctiva is quite frequently implicated in diseases because it is exposed to all types of exogenous irritants and infections. Moreover, it is prone to allergic reactions and often gets involved in metabolic disorders. Clinical features the patient complains of discomfort in the eye often associated with grittiness, heaviness and tiredness. The eye appears normal except for mild to moderate congestion towards the fornices. Treatment Symptomatic relief may be obtained by instillation of an astringent lotion like zinc sulphate (0. Etiology Chemosis occurs due to laxity of the tissue and seen in ocular and systemic diseases. The local causes of chemosis of conjunctiva include acute conjunctivitis, keratitis, corneal ulcer, iridocyclitis, orbital cellulitis, panophthalmitis and acute congestive glaucoma. It may also be associated with orbital tumors and thyroid exophthalmos owing to venous stasis. Systemic diseases such as nephritis, congestive heart failure, hypoproteinemia and allergic reactions (drug allergy, urticaria, angioneurotic edema) frequently produce chemosis of the conjunctiva. Clinical features the conjunctiva becomes swollen and appears gelatinous because of exudation from the capillaries. Symptomatic Conditions of the Conjunctiva Symptomatic conditions include hyperemia, chemosis, ecchymosis, xerosis and pigmentation of the conjunctiva. Hyperemia of the Conjunctiva Hyperemia or congestion of the conjunctival vessels may be transient or chronic. Etiology the transient hyperemia is due to irritation by a foreign body (eyelash, coal particle, concretion, etc. Adverse atmospheric conditions, especially dry dusty climate, refractive errors, metabolic disorders such as gout and diabetes, allergic 112 Textbook of Ophthalmology Treatment the management of chemosis includes treatment of the underlying cause. Treatment Generally, the subconjunctival hemorrhage gets absorbed by itself within two to three weeks. Ecchymosis of the Conjunctiva Ecchymosis or subconjunctival hemorrhage is often seen in children and aged people. Etiology Ecchymosis is found in acute conjunctivitis, especially in acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis and conjunctivitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus aegyptius (KochWeeks bacillus). Trivial trauma causes rupture of the conjunctival capillaries leading to small subconjunctival hemorrhage, while fracture of the base of skull or a violent whooping cough gives rise to large subconjunctival hemorrhage. In fracture of the base of skull, the blood seeps along the floor of the orbit and appears under the conjunctiva within 12 to 24 hours after the injury. Hemorrhages are also seen after crush injuries due to pressure on thorax and abdomen.
The recurrence is marked by anterior granulomatous uveitis symptoms neck pain buy invega 6 mg free shipping, iris nodules symptoms vitamin b deficiency invega 6mg generic, iris depigmentation and atrophy treatment quotes and sayings discount 3mg invega free shipping. Birdshot Retinochoroidopathy Birdshot retinochoroidopathy (vitiliginous chorioretinitis) occurs in the fourth decade of life medications 5 rights invega 6 mg lowest price, usually in females. The distribution of spots in the retina resembles the pattern of a birdshot scatter. Vitreous cells and optic disk edema may occur without anterior segment involvement. No effective treatment is Sympathetic Ophthalmitis It is described in the chapter on Injury to the Eye. Retinochoroidopathies Retinochoroidopathies are inflammatory disorders of unknown etiology involving choroid, choriocapillaris, retinal pigment epithelium and sensory retina. Pauciarticular onset: this type of onset shows involvement of four or fewer joints in the first 6 weeks of the disease. Complications Complications are frequent and include band keratopathy, cataract, secondary glaucoma, vitreous opacities, macular edema and hypotony. Treatment Topical short-acting cycloplegics and topical, periocular and systemic corticosteroids should be administered depending on the severity of the disease. However, most patients recover vision as the fundus lesions run a short self-limited course. The disease may progress relentlessly despite aggressive therapy with corticosteroids and immunosuppressants. Uveitis Associated with Systemic Diseases Uveitis Associated with Joint Disorders Following joint disorders are often associated with acute anterior uveitis and antigen positivity: 1. Ankylosing Spondylitis An acute nongranulomatous anterior uveitis is associated with ankylosing spondylitis in about 15% of cases. The uveitis is usually recurrent and may lead to macular edema, complicated cataract and glaucoma. The radiograph of sacroiliac region may reveal sclerosis and narrowing of the joint spaces. Acute anterior uveitis should be managed with topical cycloplegics and corticosteroids. Keratoderma blennorrhagica of palms and soles and balanitis circinata are also found. Usually the patient develops a nongonococcal urethritis which is followed by arthritis, conjunctivitis and anterior uveitis. The conjunctivitis is mucopurulent and may be associated with punctate subepithelial keratitis. An acute nongranulomatous anterior uveitis occurs independently of conjuctivitis in approximately 30% of the cases. Besides topical cycloplegics and corticosteroids, tetracycline therapy for 3 to 6 weeks may be effective in chlamydia-induced reactive arthritis. Early use of systemic immunosuppressive agents is likely to improve the long-term visual prognosis. Uveitis Associated with Respiratory Disorder Sarcoidosis Etiology Sarcoidosis is a multisystem granulomatous disease of unknown etiology. Mutton-fat keratic precipitates are distributed widely on the entire cornea and do not get collected in a classical inferior triangular manner. Etiology the etiology of the syndrome is unknown, although the basic lesion is an obliterating vasculitis. Clinical Features the classical ocular signs include episodes of acute bilateral nongranulomatous anterior uveitis usually associated with hypopyon. The posterior uveal lesions include focal retinal necrosis, macular edema and ischemic optic neuropathy. Central nervous system involvement in the form of meningitis, encephalitis and focal neurologic deficits may occur in about 25% of cases.
She reports difficulty with arm and leg strength and constant fatigue medicine just for cough 6mg invega with visa, but no fevers or sweats medications prescribed for migraines generic invega 3 mg mastercard. Which of the following studies should be performed as well to look for associated conditions He has been taking prednisone at high doses for 2 months medicine 81 generic 6mg invega with visa, and you initiated mycophenolate mofetil at the last clinic visit for a steroid-sparing effect symptoms multiple sclerosis order 6 mg invega mastercard. His symptoms were predominantly in the lower extremities and face, and he has improved considerably. Her medications include diltiazem, cyclosporine, prednisone, and mycophenolate mofetil. There is bilateral afferent pupillary defect, and she reports she cannot see out of either eye. A 77-year-old man undergoes coronary artery bypass grafting for refractory angina and three-vessel disease. His physical examination is normal except for poor performance on serial 7 subtraction and only recalling 1 or 3 objects at 15 minutes. During his complicated 3-week course of respiratory failure, he was placed on highfrequency ventilation and prone positioning necessitating paralysis and heavy sedation. While starting his physical therapy, it is noted that he has right footdrop and numbness on the lateral leg. Additional examination reveals a unilateral right motor defect in foot dorsiflexion with intact inversion. There is sensory loss of the lateral aspect of the leg below the knee extending to the dorsum of the foot. A 26-year-old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of shortness of breath and chest pain. These symptoms began abruptly and became progressively worse over 10 minutes, prompting her to call 911. Over this same period, the patient describes feeling her heart pounding and states that she felt like she was dying. It is currently about 20 minutes since the onset of symptoms and the severity has abated, although she continues to feel not back to her baseline. She denies any immediate precipitating cause, although she has been under increased stress as her mother has been hospitalized recently with advanced breast cancer. Her initial vital signs show a heart rate of 108 beats/min, blood pressure 122/68 mmHg, and respiratory rate 20 breaths/min. Reassure the patient and suggest medical and/ or psychological therapy if symptoms recur on a frequent basis. A 36-year-old man is being treated with venlafaxine 150 mg twice daily for major depression. After 2 months, his symptoms were inadequately controlled, necessitating an increase in the dose of venlafaxine from 75 mg twice daily. At that time, he was treated with fluoxetine 80 mg daily for 12 months, but found the sexual side effects difficult to tolerate. He should continue on the medication indefinitely as his depression is likely to recur. The medication can be discontinued safely if he establishes a relationship with a psychotherapist who will monitor his progress and symptoms. The medication can be discontinued safely now as his symptoms are well controlled. The medication should be switched to fluoxetine to complete 12 months of therapy, as this was previously effective for him.
Buy invega overnight. Anxiety and Globus Hystericus Symptoms - (Lump in Throat Feeling).